Machines have evolved beyond mere pattern recognition; they are now capable of creation. This leap is exemplified by Variational Autoencoders (VAEs). Unlike traditional methods that solely compress and reconstruct data, VAEs introduce controlled randomness, enabling the generation of novel, meaningful variations. Imagine a system that doesn’t just remember a face but can generate entirely new ones that have never existed.
This is achieved through the use of latent space , an invisible realm where patterns form. From the AI-created artworks to medical breakthroughs that save lives, VAEs are pushing the boundaries of deep learning. But what exactly do they do, and why are they so influential?
What Is a Variational Autoencoder?
A Variational Autoencoder is a type of neural network designed not only to compress and rebuild data but also to introduce an element of randomness. Traditional autoencoders compress input data to a lower dimension and then reconstruct it as closely as possible. VAEs enhance this process by introducing a probabilistic element to the encoding. Instead of encoding inputs to a set point, VAEs learn a distribution, allowing data representation that enables variability and generalization.
The magic of VAEs lies in their latent space—a compact form of input data that retains vital features. Through training on large datasets, VAEs learn to represent significant variations instead of merely duplicating input structures. This capability makes them extremely proficient at creating new data points, interpolating missing details, and even generating realistic images or sounds.
The procedure includes two primary stages: encoding and decoding. The encoder maps data into a probabilistic distribution, while the decoder retrieves it from samples of this distribution. By learning distributions rather than fixed encodings, VAEs produce more flexible and variable outputs, making them highly beneficial in deep learning applications.
How Do Variational Autoencoders Work?
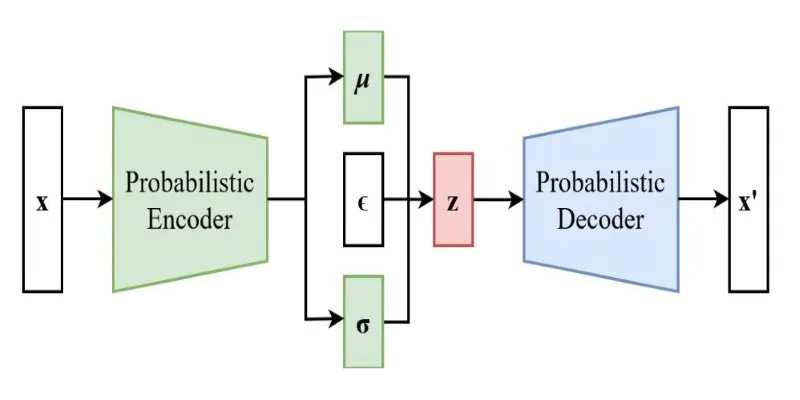
At their core, VAEs operate on mathematical principles that blend deep learning with probability theory. The encoder maps input data to a latent space using a neural network, but instead of mapping to a fixed vector, it learns a mean and variance. These values define a probability distribution from which data points are sampled. This ensures that similar inputs yield similar outputs while allowing variability.
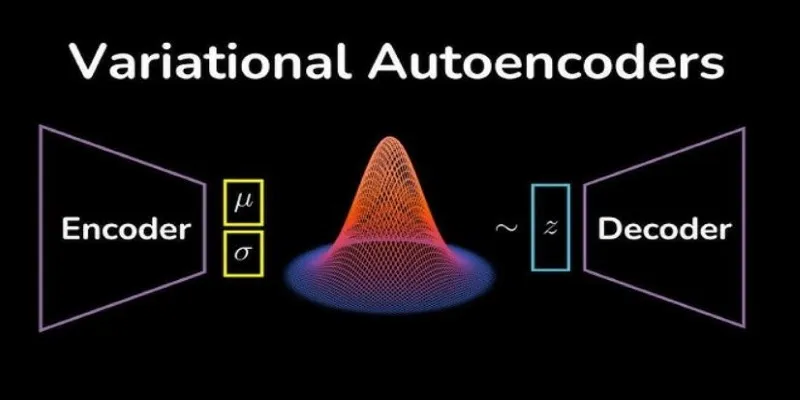
The decoder then takes these sampled values and reconstructs the data. However, VAEs don’t just optimize for reconstruction accuracy. They also use a loss function that balances two key objectives:
- Reconstruction Loss – Measures how accurately the decoded output matches the original input, ensuring that the VAE retains essential features during data compression and reconstruction.
- Kullback-Leibler (KL) Divergence – Encourages the learned latent distribution to resemble a standard normal distribution, preventing overfitting and ensuring the model generates diverse and meaningful variations of input data.
This second term is crucial because it prevents the model from collapsing into deterministic behavior. By encouraging randomness within controlled limits, VAEs can generate variations of input data rather than simply copying what they’ve seen before.
The probabilistic nature of VAEs makes them especially useful for tasks like image synthesis, where small variations in the input data should lead to smooth, meaningful variations in the output. This is why VAEs are widely used in creative AI applications, such as generating realistic human faces or designing novel chemical compounds.
Applications of Variational Autoencoders
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) have a wide range of applications across different industries, leveraging their ability to generate, analyze, and reconstruct data in meaningful ways.
Image Generation
One of the most well-known applications of VAEs is in image generation. Unlike standard neural networks that classify or detect objects, VAEs can create entirely new images based on learned patterns. This ability has been particularly useful in creating realistic avatars, improving facial recognition systems, and generating high-quality textures for video games. By learning the underlying structure of images, VAEs can produce new variations that maintain realism while introducing creativity.
Anomaly Detection
VAEs are also widely used for anomaly detection, where they help identify data points that deviate from normal patterns. Since VAEs learn the natural distribution of data, they can easily spot unusual patterns that don’t fit the expected structure. This is especially valuable in fields like fraud detection, medical diagnostics, and cybersecurity. For example, VAEs can detect fraudulent transactions in financial systems or highlight irregularities in medical scans, potentially identifying diseases in their early stages.
Drug Discovery and Molecular Design
In the medical world, VAEs have revolutionized drug discovery and molecular design. By analyzing large datasets of chemical compounds, VAEs can generate new molecular structures with desired properties. This accelerates the search for new medications, allowing scientists to explore a vast chemical space efficiently. AI-generated molecules can be used as candidates for further testing, drastically reducing the time and cost of pharmaceutical research and development.
Text and Speech Synthesis
VAEs are also instrumental in text and speech synthesis, where they help machines generate human-like conversations and convert text into realistic- sounding speech. These models improve voice assistants, chatbot responses, and language translation systems. The ability to model variability in spoken language makes VAEs an essential tool for enhancing the natural flow and tone of AI-generated speech, making human-computer interactions more engaging and realistic.
Conclusion
Variational Autoencoders do more than just process data—they reimagine it. By blending probability with deep learning, VAEs transform input into flexible, creative outputs. Whether designing lifelike images, detecting fraud, or accelerating drug discovery, they unlock possibilities beyond simple replication. Their ability to navigate latent space makes AI more than just a pattern-matcher—it becomes an innovator. As technology advances, VAEs will continue shaping industries, proving that machines can not only learn but also imagine. The question isn’t just what they can do today but how they’ll redefine creativity, security, and science in the years ahead.
 zfn9
zfn9