Wildlife conservation is vital for protecting biodiversity and maintaining ecosystem balance. Unfortunately, many species worldwide are at risk of extinction due to factors like habitat loss, poaching, climate change, and pollution.
While traditional conservation methods have been beneficial, artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a powerful tool to enhance these efforts' effectiveness and efficiency. This blog post explores how AI significantly aids in tracking endangered species and improving overall wildlife conservation.
The Role of AI in Tracking Endangered Species
Monitoring the movements and behaviors of rare species is essential for wildlife protection. Without accurate, real-time data, conservationists struggle to protect these species effectively. AI, combined with GPS tags, camera traps, drones, and other tools, is revolutionizing how we monitor endangered animals.
AI systems process vast amounts of data, enabling conservationists to track animals in the wild remotely. This non-invasive method provides an invaluable tool for observing species in their natural habitats while minimizing human impact on their behavior.
How AI Tracks Endangered Species:
- GPS Collars: Many endangered animals are equipped with GPS tags that transmit location data. AI algorithms analyze this data to provide real-time insights into the animals’ habits, migration patterns, and preferred habitats, allowing scientists to monitor large animal groups over expansive areas without physical presence.
- Camera Traps: AI-powered camera traps are strategically placed in wildlife habitats to capture images and videos of animals. Advanced AI algorithms can analyze these visuals to identify specific species, count the number of animals, and detect unusual behaviors, such as poacher presence or other threats.
- Drones: Drones equipped with AI technology capture aerial images of animal populations. By analyzing these images, AI systems can detect specific species, monitor habitat health, and track movements across large, inaccessible areas.
Benefits of AI in Tracking Species:
- Non-Intrusive Monitoring: Unlike traditional methods, AI allows for remote and non-intrusive monitoring, reducing human interaction and ensuring minimal disruption to natural behaviors.
- Real-Time Data: AI systems provide instant updates, enabling conservationists to respond swiftly to changes in animal behavior or environments.
- Improved Accuracy: By processing large data volumes, AI enhances accuracy in species identification and movement tracking, reducing human error.
Combatting Poaching with AI

Poaching remains a significant threat to endangered species, especially where wildlife habitats overlap with human settlements. AI plays a pivotal role in detecting and preventing poaching activities , enabling quicker responses to threats and reducing human-wildlife conflict.
AI-Powered Anti-Poaching Strategies:
- Predictive Patrolling: By analyzing data such as animal movement patterns, human activity, and environmental conditions, AI predicts poaching hotspots, allowing park rangers to focus patrol efforts effectively.
- Wildlife Monitoring with Drones: AI-equipped drones cover large areas, providing real-time surveillance of wildlife habitats. They detect human movement, capture images, and even track specific animals, with thermal imaging detecting poachers hidden by dense vegetation.
Protecting and Monitoring Wildlife Habitats
The protection of endangered species is closely linked to conserving their habitats. With human activities threatening ecosystems, AI helps monitor and safeguard these critical areas by analyzing environmental data.
How AI Protects Habitats:
- Environmental Monitoring: AI processes satellite imagery to track changes in habitats, such as deforestation, urbanization, or land use changes. This data helps conservationists identify and immediately address ecosystem degradation.
- Predicting Habitat Threats: AI analyzes environmental change patterns to predict potential threats to habitats, such as illegal logging or land encroachment, enabling early deployment of protection measures.
Benefits of AI in Habitat Protection:
- Efficient Monitoring: AI allows conservationists to monitor large, remote habitats more effectively by analyzing satellite images and environmental data.
- Faster Threat Identification: AI systems quickly detect habitat changes, such as deforestation or pollution, impacting endangered species’ survival.
Real-World Examples of AI in Wildlife Conservation
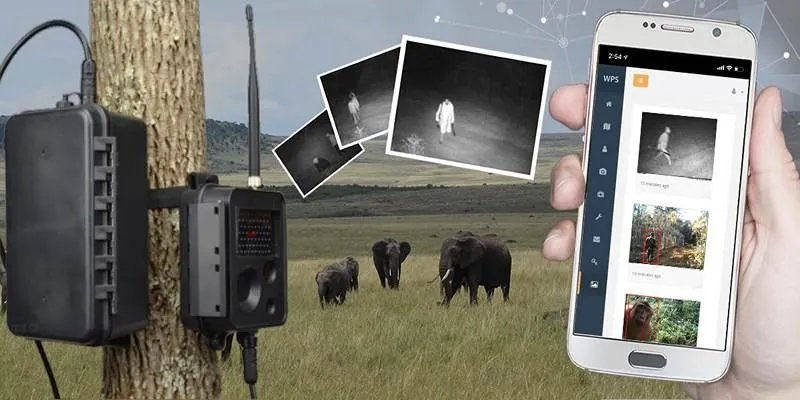

AI is already successfully used in various wildlife conservation efforts. Here are some notable examples:
- The Wildlife Protection Solutions (WPS) Project: In Africa, WPS uses AI-powered cameras and drones to monitor protected areas and detect poaching activities, preventing numerous poaching attempts and effectively tracking endangered species.
- Elephant Listening Project: This project uses AI to analyze audio recordings from forests to monitor elephants’ presence and movements, helping track populations and protect them from poaching and habitat loss.
- AI for Coral Reef Protection: Coral reefs, vital for marine biodiversity, are threatened by climate change and human activity. AI technology monitors coral health and detects early bleaching signs, allowing prompt conservation action.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence is transforming wildlife conservation by enhancing endangered species tracking, combatting poaching, and protecting habitats. AI- powered tools, such as smart surveillance systems, predictive patrolling, and environmental monitoring, are invaluable in protecting endangered species and preserving biodiversity. As technology evolves, AI will undoubtedly play an even more significant role in global wildlife conservation efforts.
 zfn9
zfn9