Data is everywhere, flooding in from smartphones, social media, sensors, and countless digital interactions. However, raw data alone isn’t valuable. It’s the ability to process, analyze, and extract insights that truly matters. This is where Big Data comes in—a concept that isn’t just about size but also about speed, complexity, and trustworthiness.
To understand Big Data, experts refer to the 5 Vs—five fundamental features that describe how data behaves and why it’s challenging to work with. These factors determine how companies, researchers, and industries transform chaotic data streams into useful insights that drive decisions and innovation.
Breaking Down the 5 Vs of Big Data
Understanding Big Data goes beyond appreciating its magnitude. The 5 Vs—Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity, and Value—highlight the complexities of processing vast amounts of data and deriving useful insights from it.
Volume: The Sheer Size of Data
The most prominent dimension of Big Data is volume. Every minute, millions of messages, emails, and searches are generated. Social media alone contributes an astonishing quantity, as individuals constantly post photographs, videos, and updates. Enterprises, governments, and institutions receive vast amounts of data that must be stored, processed, and analyzed.

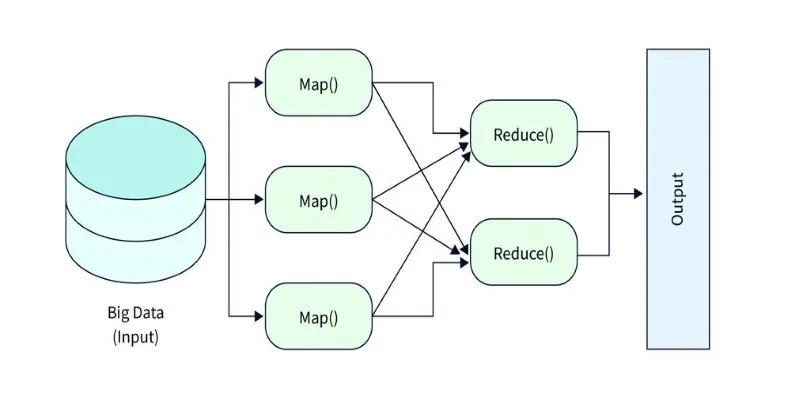
Advancements in storage technology have supported this growth. Distributed storage systems, data lakes, and cloud computing enable the storage of exabytes or petabytes of data. But the challenge is not just storing data; it’s deciphering it. Such large datasets are difficult for traditional databases, leading to more complex storage and processing solutions like Hadoop and NoSQL databases.
For businesses, leveraging vast amounts of data can translate to enhanced insights, improved decision-making, and the ability to offer customized products and services. Without the proper tools, excessive information can become a hindrance rather than an asset.
Velocity: The Speed at Which Data Moves
Data moves at lightning speed. In today’s world, real-time data processing is increasingly important. Whether it’s stock market transactions, live sports updates, or instant messaging, information flows at an incredible pace. Businesses must analyze data as it arrives rather than storing it for later review.
Traditional data processing methods often struggle with this requirement. By the time old data is processed, new information has already changed the landscape. Modern analytics systems therefore use technologies like stream processing and in-memory computing to handle high-speed data. Companies like Amazon, Google, and Netflix rely on fast data processing to provide real-time recommendations, detect fraud, and enhance user experiences.
Speed is critical in industries like healthcare and finance. A delay in detecting a cyberattack or diagnosing a medical condition can have serious consequences. Velocity ensures insights arrive when needed, not after the opportunity has passed.
Variety: The Many Forms of Data
Data doesn’t come in one neat format. In the past, information was mostly structured—think spreadsheets, customer records, and sales reports. Today, data exists in countless forms. Social media posts, videos, images, emails, and sensor readings all contribute to the growing pool of information, making data more complex and harder to manage.
Structured data, found in traditional databases, is easy to analyze due to its fixed format. However, most data today is unstructured or semi-structured, meaning it doesn’t fit neatly into tables. Emails, documents, and multimedia files require different processing techniques.
Businesses must adapt to this complexity by using tools that can handle diverse data types. AI-powered algorithms, natural language processing, and image recognition help companies make sense of messy, unstructured information. Without the ability to process various data types, organizations risk missing valuable insights hidden within their datasets.
Veracity: Ensuring Data Accuracy and Trustworthiness
Not all data is reliable. In an era of misinformation, data quality is a major concern. False information, duplicate records, and incomplete datasets can lead to bad decisions. Veracity refers to the accuracy and trustworthiness of data. If organizations can’t rely on their data, their conclusions and strategies will be flawed.

Data cleaning and validation techniques are crucial for ensuring reliability. This involves removing inconsistencies, filling in missing values, and verifying sources. Businesses also use AI and machine learning to detect patterns that indicate fraud, errors, or manipulation.
Poor-quality data can be disastrous for industries like healthcare and finance, where precision is crucial. Errors in a hospital’s patient records could lead to incorrect treatments, while inaccurate financial data could cause costly mistakes for investment firms. Ensuring veracity is essential for maintaining trust in data-driven decisions.
Value: Turning Data into Insights
The final and perhaps most important “V” is value. Collecting and analyzing data is meaningless unless it provides real benefits. The ultimate goal of Big Data isn’t just to store vast amounts of information—it’s to generate insights that drive progress, efficiency, and innovation.
Companies invest in data analytics to improve decisions, enhance customer experiences, and boost efficiency. Retailers analyze shopping trends to manage inventory, healthcare providers track disease patterns for better treatment, and sports teams use data to refine strategies, all leveraging insights to gain a competitive edge.
However, extracting value from data requires the right approach. Companies need skilled analysts, advanced machine learning models, and powerful visualization tools to interpret complex datasets. Without proper analysis, data remains just a collection of numbers with no practical use.
Conclusion
The 5 Vs of Big Data—Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity, and Value—define how organizations process and utilize massive amounts of information. Effectively managing these factors enables businesses to extract meaningful insights, improve efficiency, and make data-driven decisions. As technology advances, the ability to handle Big Data will become even more critical, shaping industries and driving innovation. Organizations that embrace these principles will stay ahead, turning raw data into valuable knowledge that fuels progress and competitive advantage in an increasingly data-driven world.
 zfn9
zfn9