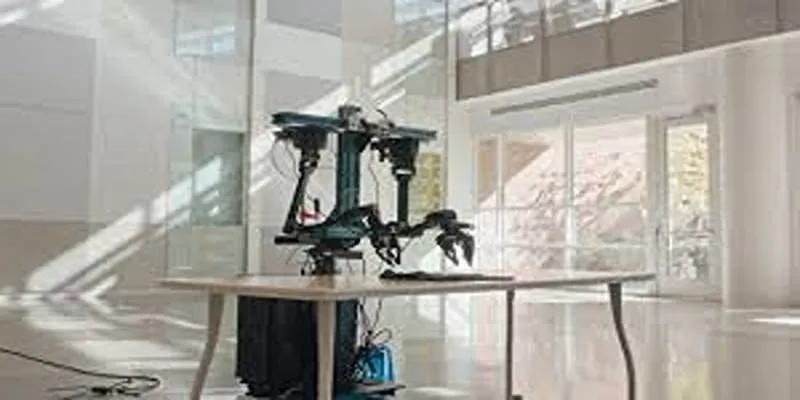
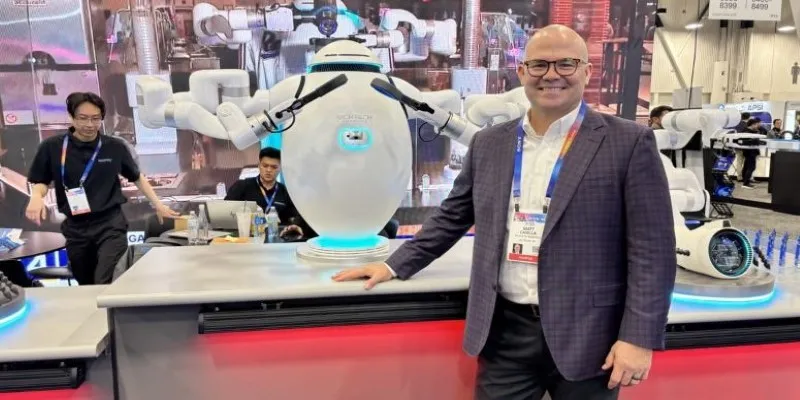
OpenAI has quietly entered the robotics arena by filing a trademark application for a humanoid robot. This strategic move highlights the company’s growing interest in extending artificial intelligence beyond the realm of software into the physical world, where machines and humans interact more directly. Known for its advanced language models and image generators, OpenAI’s trademark for a humanoid robot suggests the company might be designing machines capable of walking, moving, and potentially assisting in everyday settings. This development leads many to wonder about the future of robotics and AI collaboration.
What Does the Trademark Imply?
The trademark filing, discovered in the United States Patent and Trademark Office’s public records, hints at a physical product under OpenAI’s name. While the specifics are sparse, the categories listed include robots designed to interact with people, mechanical and AI-based control systems, and devices mimicking human motions.

OpenAI has never publicly announced a humanoid project, making this filing particularly intriguing. It’s common for tech companies to file trademarks before revealing products to protect intellectual property during development. While this doesn’t confirm an imminent release, it signifies OpenAI’s serious commitment to the field of humanoid robotics.
Why a Humanoid Robot Aligns with OpenAI’s Vision
OpenAI’s mission of teaching machines to understand and generate human-like outputs naturally extends to humanoid robots. These robots could blend physical presence with sophisticated AI, moving beyond screens and keyboards to interact face-to-face with people.
This concept aligns with the increasing demand for service robots in healthcare and customer service. Robots that can understand instructions and engage politely could fill labor gaps in industries reliant on human interaction. For example, in elder care, robots might assist with daily tasks, while in retail, they could greet customers and manage inventory.
OpenAI’s models can already conduct detailed conversations and solve problems. A humanoid form could enhance their utility by integrating them more deeply into the physical world, transforming machines from mere tools to collaborative partners.
Potential Impact on the Robotics Industry
OpenAI’s entry into the humanoid robot space introduces fresh competition to a field with major players like Boston Dynamics, Tesla, and Figure. While each company has its approach, none have perfected a robot that truly integrates into human environments.

OpenAI’s advantage lies in its software intelligence. Its advanced language models could bring a new level of conversational ability to robotics, setting a higher standard. Current humanoid robots struggle with flexible communication, often relying on rigid scripts. OpenAI’s technology might enable robots to adapt to open-ended situations and unpredictable human behavior.
There’s also potential for innovative learning methods. OpenAI’s AI systems use reinforcement learning, allowing robots to learn from observation and feedback rather than hard-coded programming. This adaptability could make humanoids more practical in dynamic real-world environments.
Despite these advantages, challenges remain, including engineering concerns about balance, energy efficiency, safety, and cost. OpenAI’s success may hinge on strategic hardware partnerships.
Anticipating OpenAI’s Next Moves
Now that the trademark is public, speculation about OpenAI’s plans is likely to increase. A trademark doesn’t guarantee an immediate product launch, as companies often file years in advance. However, OpenAI’s rapid development history suggests work on the robot is underway.
Key questions include whether OpenAI will target general-purpose assistance or specific roles. A home assistant robot would need to be friendly and capable of household chores, while business models require reliability and professionalism. The trademark wording leaves both options open, describing a versatile robot for multiple settings.
Another possibility is showcasing a prototype to demonstrate concepts rather than a complete product. Prototypes can highlight potential to investors and the public, paving the way for a production-ready version over time.
Conclusion
OpenAI’s trademark filing for a humanoid robot signals its intention to integrate artificial intelligence into daily life through physical forms. By merging its language models with humanlike machines, OpenAI could revolutionize robots in homes, workplaces, and public spaces. Although an immediate launch seems unlikely, this move indicates OpenAI’s vision of AI stepping beyond screens and into the real world, sparking anticipation about future developments.
For more on AI advancements, check out OpenAI’s official blog or explore recent breakthroughs in AI.
 zfn9
zfn9