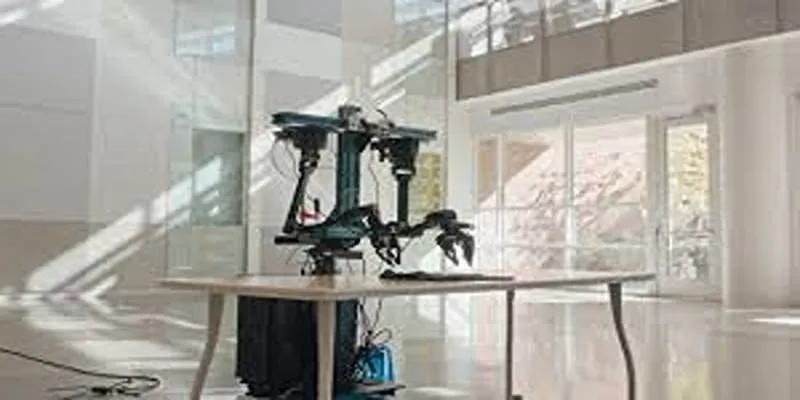
At the Shanghai Auto Show, visitors encountered an extraordinary sight—a humanoid robot dressed as a dealership staff member, welcoming potential customers and providing detailed explanations about the cars on display. This innovative robot isn’t just a gimmick; it represents a significant experiment in merging artificial intelligence with human-like interaction in commercial settings.
How the Robot Works and What It Can Do
The humanoid robot showcased at the Shanghai Auto Show is specifically developed and trained to act as a knowledgeable car salesperson. Equipped with sensors, cameras, and advanced speech recognition software, it greets visitors, asks questions to understand their preferences, and explains car features in detail. Its artificial intelligence is designed to understand both spoken questions and non-verbal cues, making its interactions feel more personal than a static information kiosk.

Developers claim the robot possesses an extensive automotive database, covering specifications, model comparisons, pricing, financing options, and maintenance advice. This allows it to guide customers through complex choices seamlessly, either by showing digital displays or leading them to specific models. During its Shanghai debut, the robot interacted in both Mandarin and English, highlighting its focus on multilingual environments.
Why Automakers Are Interested in Humanoid Sales Robots
The decision to present a humanoid robot trained as a car salesperson at one of the world’s largest auto shows is strategic. As customer expectations evolve, and with more visitors exploring showrooms just to compare before purchasing online, automakers see value in offering a consistent, always-available source of guidance.
One key reason is consistency. Unlike humans who might tire or become distracted, a robot can deliver the same standard of information and courtesy throughout a long workday. It can also assist during peak times, when visitor numbers exceed available sales staff. For some customers, especially younger generations comfortable with technology, interacting with a robot may even feel more approachable.
For automakers, there’s the added benefit of data collection. Every interaction with the humanoid robot generates valuable insights: common questions, popular models, and showroom navigation patterns. This data can be analyzed to refine marketing strategies or improve showroom layouts. The robot conducts this data collection while adhering to privacy guidelines, anonymizing customer data when necessary.
Reactions from Visitors and Industry Observers
At the Shanghai Auto Show, the humanoid robot attracted a steady crowd. Many visitors lined up to interact with it, with reactions ranging from amused surprise to genuine appreciation. Some praised its depth of knowledge, finding it easier to get quick answers without feeling pressured. Others admitted it still felt unusual to discuss car loans and fuel economy with a machine that looked vaguely human.

Industry experts see both promise and limitations. On the positive side, a robot never forgets product details and can handle multilingual customers more effectively than some staff members. It can be particularly beneficial in areas where recruiting and training good salespeople is challenging, especially in large, busy cities. However, some argue that buying a car is often an emotional decision, where trust and rapport are crucial—elements hard to replicate even with the most advanced robot.
Concerns about job impact also surfaced. While companies presenting the robot were quick to emphasize its role as an assistant, not a replacement, some visitors worried about automation in retail roles. However, for many experiencing it at the show, the robot appeared more as an advanced tool rather than a full replacement.
The Future of Humanoid Robots in Showrooms
Seeing a humanoid robot trained as a car salesperson in a showroom is still new, but the Shanghai Auto Show example suggests it might become more common. As technology advances, developers expect robots to handle even more natural conversations, pick up on subtle emotions, and provide tailored suggestions. The goal is not only to answer questions but also to make the car shopping process smoother and less intimidating for customers.
Manufacturers are exploring ways to integrate these robots alongside human staff, allowing them to take on routine tasks and free up humans for more nuanced conversations. For smaller dealerships, even one such robot could extend service hours or cover staff gaps. In larger flagship locations, multiple robots could guide visitors through different showroom sections or accompany them to view vehicles outside.
Simultaneously, designers are working to make robots appear less uncanny and more approachable while enhancing their ability to interpret speech and gestures in noisy environments. The ultimate aim is to strike a balance where technology enhances human service rather than competing with it.
Conclusion
The humanoid robot trained as a car salesperson at the Shanghai Auto Show illustrates how artificial intelligence is becoming a part of everyday retail. Blending customer service with robotics, it extends beyond automating tasks to influence how people connect with brands. While unlikely to replace human staff entirely, it provides consistent assistance, multilingual communication, and valuable insights. Its debut signifies growing interest in using human-like machines to enhance showroom experiences and customer interactions.
 zfn9
zfn9