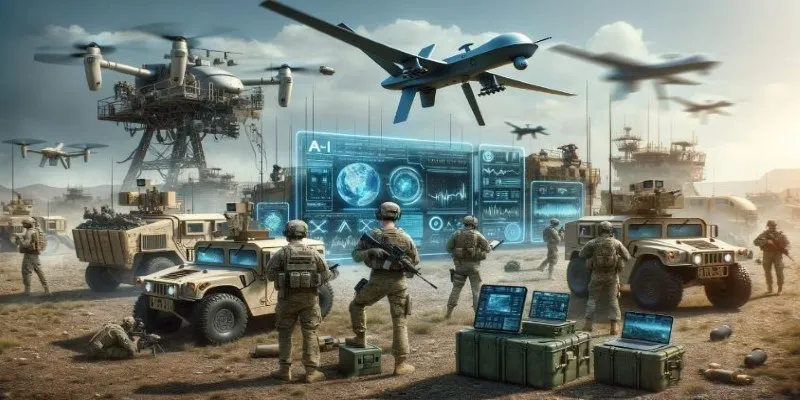
For centuries, warfare was dictated by human decisions—soldiers and commanders crafted every battlefield move. However, the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming this reality at a rapid pace. AI in warfare is no longer confined to the realm of science fiction; it is active and continuously evolving. Machines are not merely assisting soldiers; they are making critical life-and-death decisions. Unlike past advancements in weaponry, AI introduces a new level of autonomy, allowing machines to identify targets and act independently of human control.
This shift ignites a global debate around ethics, safety, and the future of warfare. Autonomous weapons raise challenging questions about accountability, control, and global security—issues that could redefine warfare, human rights, and military strategies for generations.
What Are Autonomous Weapons?
Autonomous weapons are systems capable of operating independently without human intervention once activated. These systems utilize sensors, algorithms, and machine learning to select and target based on predefined criteria. Examples include unmanned drones that autonomously attack or defense systems that detect and neutralize threats without waiting for human authorization.
The crux of this debate centers not on the physical form of these machines but on their decision-making capabilities. Can machines be trusted to discern between enemy combatants and civilians? These questions highlight a critical concern: once an autonomous weapon is deployed, meaningful human control might be an illusion at crucial moments.
Proponents argue that autonomous weapons could reduce human casualties by removing soldiers from hazardous situations. Machines, immune to fear, fatigue, or emotion, theoretically make more calculated decisions in dynamic combat environments. However, this assumption hinges on the belief that technology can entirely replace human judgment—a notion many experts contest.
Ethical Concerns and Global Security Risks
The integration of AI in warfare presents unprecedented ethical challenges. Traditional warfare is already chaotic and tragic, but it is conducted under the rules, training, and moral judgment of human soldiers. Machines, regardless of their sophistication, lack consciousness and empathy. In cases of malfunction or misidentification, who bears responsibility? The machine? Its developers? The military commanders?

Beyond individual errors, there is a broader concern that autonomous weapons might lower the threshold for initiating conflicts. With machines capable of fighting battles with reduced human risk, political leaders might be more inclined to engage in warfare. This could lead to machine-dominated battles impacting real human populations.
Experts also caution against the misuse of autonomous weapons by authoritarian regimes or terrorist groups. As the technology becomes more affordable and accessible, controlling its use becomes increasingly difficult. The proliferation of autonomous weapons risks destabilizing already fragile regions, making conflicts more unpredictable and challenging to contain. For more insights on the implications of AI in warfare, consider exploring resources provided by authoritative organizations such as the [International Committee of the Red Cross](https:/www.icrc.org/en/document/artificial- intelligence-and-autonomous-weapons-systems).
Additionally, an AI arms race poses a significant threat. If one nation deploys advanced autonomous weapons, others may feel compelled to follow suit to maintain military parity, fostering a dangerous cycle of competition with little room for ethical consideration or regulation.
The Case for Regulation and Human Control
Amid the rapid development of AI in warfare, numerous experts and organizations advocate for stringent international regulations. Some go as far as calling for a complete ban on fully autonomous weapons. The Campaign to Stop Killer Robots, a coalition of non-governmental organizations, is a prominent voice in the movement to ban autonomous weapons entirely.
Advocates for regulation emphasize the necessity of maintaining “meaningful human control” over decisions involving the use of force. This principle asserts that humans should remain directly involved in decisions when lethal actions are considered. The idea is straightforward: machines should support humans, not replace them in making life-and-death decisions.
The United Nations has engaged in discussions about potential treaties and agreements to regulate the development and use of autonomous weapons. However, achieving a global consensus is challenging. Some nations argue that autonomous weapons offer military advantages and should not be outright banned. Others worry that without clear regulations, autonomous weapons could be widely misused.
Interestingly, this debate extends beyond law and policy into the realm of human identity. Delegating lethal decisions to machines forces us to reevaluate what it means to be human in warfare. Is keeping soldiers safe worth sacrificing moral accountability? Does using machines for lethal actions erode our collective sense of responsibility?
These questions are complex, but addressing them is crucial to prevent leaving the future of warfare solely in the hands of technology without human guidance.
The Future of AI in Warfare
AI in warfare is not merely a passing trend—it is reshaping the very nature of armed conflict. The debate surrounding autonomous weapons is among the most critical discussions of our era. Decisions made today will shape how future wars are conducted and how humanity balances technological advancement with ethical responsibility.

On one hand, AI can enhance soldier protection, improve defense systems, and offer strategic advantages. On the other hand, autonomous weapons challenge fundamental values of human life, dignity, and accountability. Striking a balance requires wisdom, caution, and global collaboration.
If left unchecked, the development of autonomous weapons may lead to a future where warfare becomes more automated, detached, and dehumanized. Without stringent regulation and clear moral boundaries, technology risks outpacing our ability to control it.
Conclusion
AI in warfare presents a stark choice: Will technology be used to make war more humane and controlled, or will machines dominate conflicts without human oversight? The answer will shape not only the future of warfare but the future of humanity itself. How we address this issue today—with regulation, global cooperation, and ethical responsibility—will determine whether AI in warfare becomes a tool for protecting life or a force that threatens it. The path forward must be guided by innovation and humanity’s deepest values and respect for life.
 zfn9
zfn9