Amazon S3, or Simple Storage Service, has become a go-to cloud storage solution since its debut in 2006. It offers a dependable way to store and access data on the web, whether for hosting website files, maintaining backups, or storing application data. Its popularity stems from its simplicity—easy to set up, scalable, and reliable. Individuals and businesses use it for everything from small projects to global operations. This guide explains what Amazon S3 is, how it functions, and why it’s trusted by many.
What is Amazon S3, and How Does It Work?
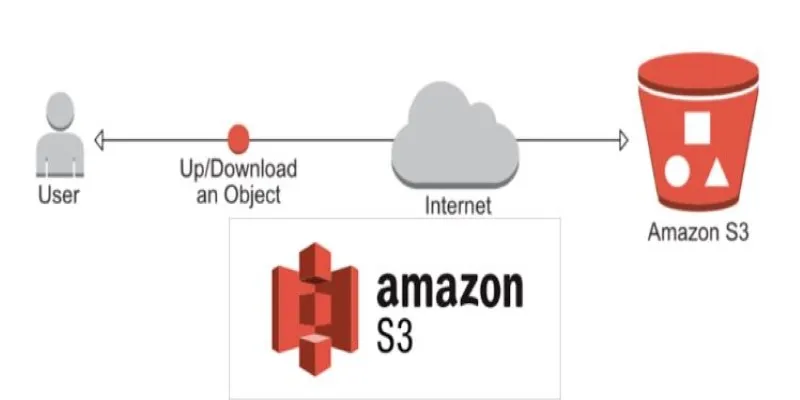
Amazon S3 is a cloud-based service that allows you to store and access your data anytime, anywhere, as long as you have an internet connection. Unlike the typical folder-and-drive structure on a computer, S3 organizes your files into “buckets,” and each file, called an “object,” gets a unique key. This straightforward system makes it easy to track everything, no matter how much you upload.
What makes S3 stand out is its robust data protection. Every file you save is automatically copied across multiple servers in Amazon’s regional data centers. Even if one server or building fails, your files remain safe and accessible. Amazon even boasts eleven nines of durability, meaning the chance of losing a file is almost zero.
You have full control over who can access your data. Files can be entirely private, shared via secure links, or made public if desired. This flexibility supports everything from sensitive backups to making open files available on a website.
Storage Classes and Pricing
Amazon S3 offers various storage classes tailored to your data usage:
- Standard: Ideal for frequently accessed files, like website media or active project files.
- Infrequent Access (IA): Lower costs for less-used data, keeping files accessible when needed.
- Glacier and Glacier Deep Archive: Economical options for archival data you rarely access.
Pricing depends on more than just storage volume. It also considers access frequency, data transfer out, and the number of operations performed. However, it’s pay-as-you-go, meaning you only pay for what you use. Many users create cost estimates with Amazon’s calculator before committing large amounts of data.
S3 helps save money over time by automating storage changes. You can set lifecycle rules to transition files to cheaper classes as they age—like moving backups from Standard to Glacier after 30 days. This keeps costs predictable without constant manual adjustments.
Features and Use Cases
Amazon S3 includes features that extend beyond simple storage:
- Versioning: Keeps old copies of files instead of deleting them outright, useful if you overwrite something by mistake.
- Encryption: Protects data both in transit and at rest, with options to manage it yourself or let Amazon handle it.
- Access Control: AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) allows fine-grained control over who can view or change specific files or buckets.

S3 integrates seamlessly with other AWS services. Many websites use it to serve static content like images and downloads. Others use it as a data lake for analytics, a place to store IoT data, or a backup target for servers. It scales automatically, so whether you store a few files or petabytes of data, it performs consistently.
Reliability is a key reason people choose S3. Data is distributed across multiple facilities within a region, ensuring high availability. For added resilience, cross-region replication enables you to copy data to another part of the world, making it a dependable choice for both business-critical and personal projects.
Getting Started with S3
Setting up and using Amazon S3 is straightforward, even for beginners. You start by creating a bucket in your chosen AWS region. Then, upload your files using the web console, AWS CLI (command-line interface), or programmatically via APIs. Permissions can be adjusted to allow access only to you, specific users, or the public.
For developers, S3 integrates seamlessly with other AWS services. You can connect it to CloudFront for faster content delivery, use Lambda to process files automatically upon upload, or hook it into AWS Athena to query stored data directly. These integrations make it easier to build advanced workflows without separate storage or processing systems.
For those concerned about security, Amazon provides tools to audit access logs, enforce encryption policies, and set up alerts for unauthorized permission changes or file deletions. Many controls can be automated, so constant monitoring isn’t necessary.
For anyone already using AWS for compute or networking, S3 is a natural fit. Its simplicity masks a lot of engineering behind the scenes, allowing you to focus on your work without worrying about hardware or maintenance. Even for those not tied to AWS, it offers a reliable and flexible cloud storage option with unmatched durability and global reach.
Conclusion
Amazon S3 stands out as a dependable and flexible cloud storage service that’s easy to set up and manage. With its range of storage classes, built-in security, and straightforward pricing, it suits both small personal projects and large enterprises. Its high durability and seamless integration with other tools make it an attractive choice for storing and accessing data. Whether you’re hosting files for a website, archiving records, or building an analytics system, Amazon S3 offers a practical way to keep your data safe, accessible, and scalable without unnecessary complexity or steep learning curves.
 zfn9
zfn9