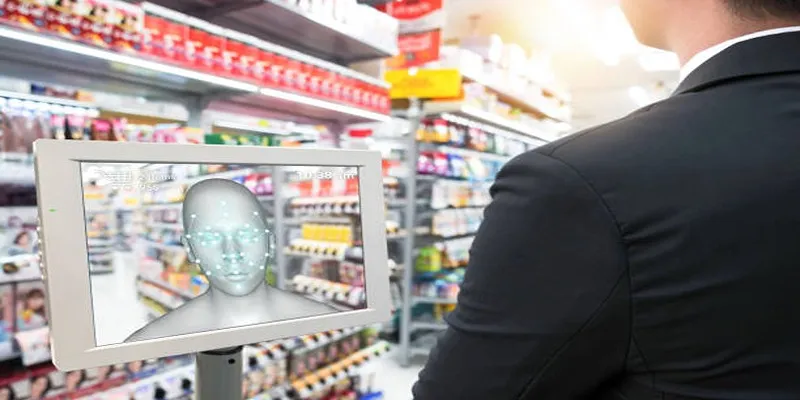
Artificial intelligence (AI) has revolutionized surveillance, enabling advancements like face recognition, behavior analysis, and real-time monitoring. These AI-driven systems are employed by governments and businesses to enhance public safety and prevent crimes. However, the widespread use of AI surveillance raises significant privacy concerns, such as potential data misuse and the erosion of personal privacy.
While AI improves security, excessive surveillance can lead to ethical and legal dilemmas. Finding a balance between security and privacy is crucial to prevent abuse. Responsible monitoring requires transparency, regulations, and ethical AI applications. Understanding these elements is essential for developing an AI-driven tracking system that is both fair and secure.
How AI is Used in Surveillance
AI plays a critical role in surveillance through various applications that enhance monitoring, security, and crime prevention. Key applications include:
- Facial Recognition: AI-driven cameras use facial recognition to identify individuals in real-time. This technology is utilized in airport security screenings, law enforcement investigations, and corporate security measures.
- Behavior Analysis: AI algorithms analyze patterns in human behavior to detect suspicious activities, such as loitering in restricted areas or unusual crowd movements.
- License Plate Recognition (LPR): AI-powered surveillance devices read and record license plates, aiding law enforcement and traffic control.
- Crowd Monitoring: AI surveillance assists authorities in managing large gatherings, monitoring protests, and overseeing public events to prevent security threats.
- Intrusion Detection: AI-based security systems detect unauthorized access to restricted areas, alerting authorities to potential security breaches.
- Object Detection: AI identifies abandoned objects in public spaces, helping security personnel respond to potential threats, such as unattended bags in airports and train stations.
These technologies enhance security and accelerate response times, improving surveillance systems’ ability to prevent and address security issues. However, their widespread use raises privacy concerns and the risk of over- surveillance.
Privacy Concerns in AI Surveillance
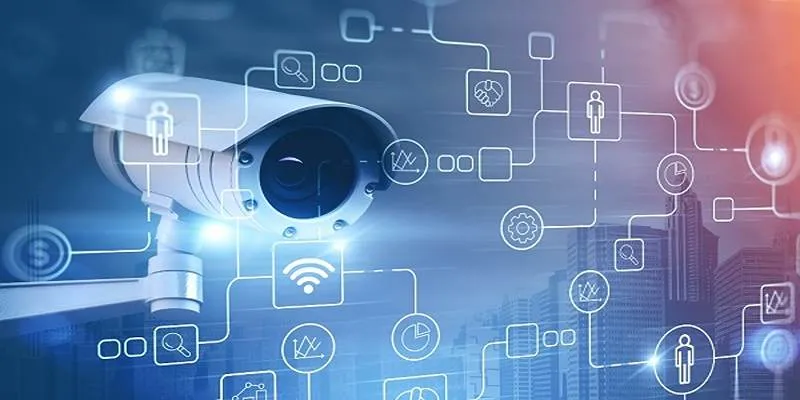

AI-powered surveillance presents several privacy challenges , leading to concerns over mass surveillance, data misuse, and individual rights. Key privacy concerns include:
- Mass Surveillance: AI-driven surveillance systems continuously monitor public and private spaces, heightening the risk of excessive government and corporate control over citizens.
- Unauthorized Data Collection: AI surveillance collects vast amounts of personal data without individuals’ explicit consent, raising ethical and legal concerns.
- False Identifications: Facial recognition technology has faced criticism for inaccuracies, resulting in false identifications and wrongful accusations.
- Loss of Anonymity: Continuous tracking by AI-powered security cameras makes it nearly impossible for individuals to maintain anonymity in public spaces.
- Unclear Data Retention Policies: Many organizations lack transparency regarding how long they retain surveillance footage, who has access, and how it is used, leading to concerns about misuse.
- Lack of Accountability: In many cases, AI surveillance systems operate without proper oversight, making it challenging to hold authorities accountable for privacy violations.
As individuals and organizations grapple with these privacy concerns, the debate over finding a middle ground between security and civil liberties intensifies. Without proper regulations, AI surveillance risks ethical violations and misuse of personal information.
Ethical Challenges in AI Surveillance
AI surveillance raises several ethical concerns, particularly related to human rights, fairness, and accountability. Major ethical challenges include:
- Bias in AI Algorithms: AI facial recognition has been criticized for racial and gender biases, leading to discriminatory outcomes in law enforcement and security screenings.
- Misuse by Governments and Corporations: Some governments and corporations use AI surveillance to suppress dissent, monitor political activities, or target specific groups.
- Over-Policing Certain Communities: AI-driven surveillance systems disproportionately target certain neighborhoods, resulting in unfair profiling.
- Data Security Risks: If not properly protected, AI surveillance data can be hacked or leaked, exposing sensitive information to cyber threats.
Balancing Security and Privacy in AI Surveillance
Achieving a balance between security and privacy is essential for responsible AI surveillance. Implementing the following measures can help mitigate privacy risks while maintaining security :
Strengthening Data Protection Laws
Governments should enforce clear and strict data protection laws to regulate how AI surveillance systems collect, store, and use personal information. These laws should ensure:
- Data is collected transparently and solely for security purposes.
- Individuals have control over their personal information.
- Strong penalties are imposed for unauthorized data use.
Using AI for Targeted Surveillance

Rather than employing mass surveillance, AI should focus on specific security threats, targeting identified risks instead of indiscriminately monitoring entire populations.
Transparency in AI Surveillance Practices
Organizations must disclose how AI surveillance systems operate, including:
- The purpose of data collection.
- The duration for which data is stored.
- Who has access to surveillance data and how it is used.
Reducing Bias in AI Algorithms
To prevent discrimination, AI systems must be trained on diverse datasets, regularly audited for fairness, and tested to eliminate biases that may affect certain groups.
Independent Oversight and Regulation
Independent bodies should oversee AI surveillance programs to ensure:
- Proper checks and balances are in place.
- Surveillance technologies comply with privacy laws and ethical guidelines.
- Misuse of surveillance data is prevented.
Conclusion
AI surveillance offers numerous benefits in enhancing security, preventing crimes, and improving law enforcement efforts. However, it also raises concerns about mass surveillance, data misuse, and ethical violations. Striking the right balance between security and privacy is crucial to ensure that AI-powered surveillance systems do not infringe on individual rights. Governments, businesses, and technology developers must adopt strict regulations, enhance transparency, and implement ethical guidelines to ensure AI surveillance serves its intended purpose without becoming a tool for privacy invasion.
 zfn9
zfn9